Post: Water Contamination And Purification
Water contamination can occur to city water supplies, well water supplies, and fresh water sources, such as lakes, streams, and rivers. Consuming contaminated water can cause numerous effects.
Are you concerned about contaminants in your home’s water? Do you know if you can safely drink the water in your home?
Signs/Symptoms of Drinking Contaminated Water
First, it’s important to know the health effects people experience may or may not present themselves immediately. Further, factors such as the overall health, age, and physical condition of the person determine the extent of the actual effects experienced. Some of the more commonly reported problems experienced from drinking impure water include, but are not limited to, the following waterborne illnesses:
● Gastrointestinal Problems
● Diarrhea
● Nausea
● Intestinal or Stomach Cramping
● Intestinal or Stomach Aches and Pains
● Dehydration
● Death
Keep in mind, just because no signs or symptoms are experienced, it does not mean there are no potential long term effects. For example, if water sources are contaminated with radium or radon gas, you might not notice an immediate health effect. However, long-term exposure has been linked to cancer and heart disease. Other possible contaminants found in tainted water sources are:
● E. coli Bacteria
● Coliform Bacteria
● Nitrates
● Lead
● Fluoride
● Arsenic
● Radium
● Radon
● Pharmaceuticals
● Herbicides
● Pesticides
● Chemicals
● Fecal Matter
● Microbial Pathogens
● Parasites
● Viruses
● Petrochemicals
Contaminants can enter water supplies through various means. For instance, the ground absorbs contaminants. The absorbed materials contaminate ground water sources, broken pipes, and excess water run-off during heavy rain periods.
Does Dirty/Contaminated Water Smell?
In some cases the water could smell or taste different. However, many contaminants have no taste or odor. This leaves no indication of contamination.
Will Boiling Water Help Make It Safe?
Boiling does kill most types of parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Additionally, it increases concentrations of other contaminants due to evaporation of water.

Water Purification by Reverse Osmosis
Pressure forces it through a semipermeable membrane. Water flows from the more concentrated side (more contaminants) of the RO membrane to the less concentrated side (feweReverse osmosis removes contaminants from unfiltered water, or feed water, when r contaminants) to provide clean drinking water. The fresh water produced is called the permeate. The concentrated water left over is called the waste or brine.
A semipermeable membrane has small pores that block contaminants but allow water molecules to flow through. In osmosis, water becomes more concentrated as it passes through the membrane to obtain equilibrium on both sides. Reverse osmosis, however, blocks contaminants from entering the less concentrated side of the membrane. For example, when pressure is applied to a volume of saltwater during reverse osmosis, the salt is left behind and only clean water flows through.
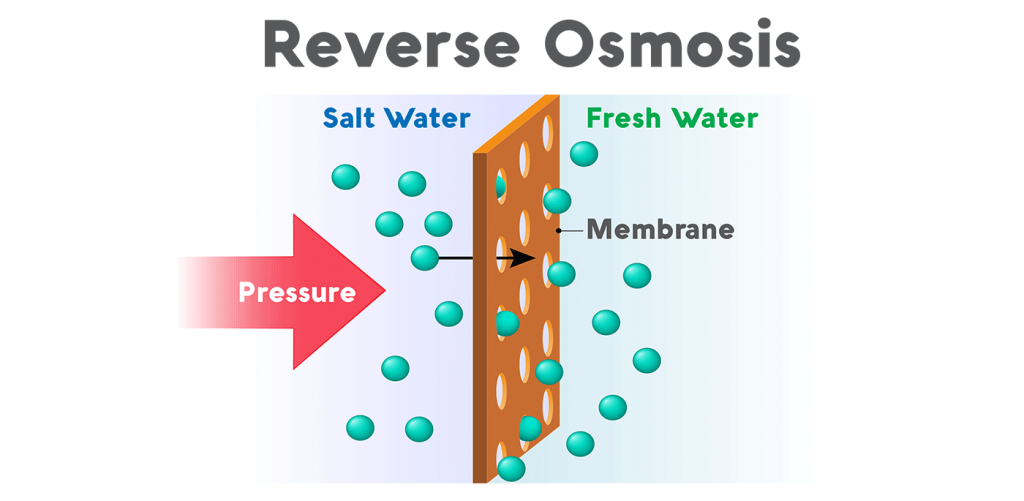
How does a reverse osmosis system work?
A reverse osmosis system removes sediment and chlorine from water with a prefilter before it forces water through a semipermeable membrane to remove dissolved solids. After water exits the RO membrane, it passes through a post-filter to polish the drinking water before it enters a dedicated faucet. Reverse osmosis systems have various stages depending on their number of pre-filters and post-filters.
Stages of RO systems
The RO membrane is the focal point of a reverse osmosis system, but an RO system also includes other types of filtration. RO systems are made up of 3, 4, or 5 stages of filtration.
Every reverse osmosis water system contains a sediment filter and a carbon filter in addition to the RO membrane. The filters are called either prefilters or postfilters depending on whether water passes through them before or after it passes through the membrane.
Each type of system contains one or more of the following filters:
Sediment filter: Reduces particles like dirt, dust, and rust
Carbon filter: Reduces volatile organic compounds (VOCs), chlorine, and other contaminants that give water a bad taste or odor
Semi-permeable membrane: Removes up to 98% of total dissolved solids (TDS)
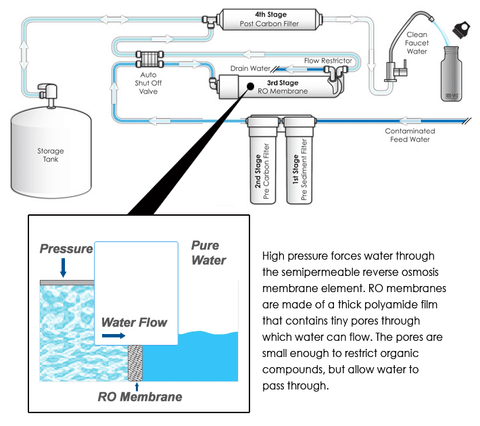
When water first enters an RO system, it goes through pre-filtration. Pre-filtration typically includes a carbon filter and a sediment filter to remove sediment and chlorine that could clog or damage the RO membrane.
Next, water goes through the reverse osmosis membrane where dissolved particles, even too small to be seen with an electron microscope, are removed.
After filtration, water flows to the storage tank, where it is held until needed. A reverse osmosis system continues to filter water until the storage tank is full and then shuts off.
Once you turn on your drinking water faucet, water comes out of the storage tank through another pos filter to polish drinking water before it gets to your faucet.
Why do you need an RO storage tank?
An RO storage tank holds reverse osmosis water so you have plenty to use when you need it. A reverse osmosis system makes water slowly. It takes one minute to produce two to three ounces of RO water. If you were to turn on your faucet for a glass of water at the actual membrane production rate, then you would have to wait at least 5 minutes for it to fill. With a storage tank, your glass fills instantly.
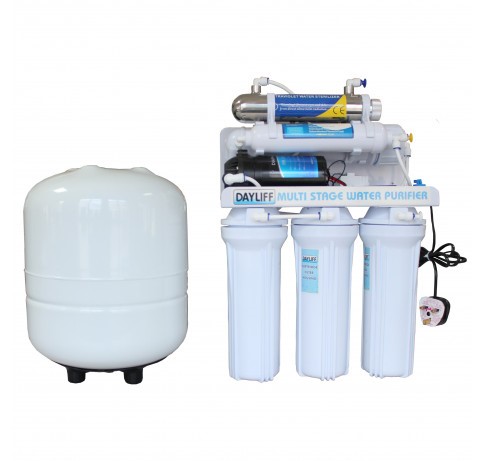
The Under sink Reverse Osmosis System.
The RO (Reverse Osmosis) is also known as an Under-sink RO since it can fit conveniently under a normal sink in any house. It utilizes reverse osmosis technology to produce totally pure water from borehole and municipal / city council water sources. Specification includes three stage pre-treatment through sediment and carbon filters, Reverse Osmosis treatment, final treatment with carbon filter for taste and UV sterilizer as the sixth stage. It also features Hidrotek / Filmtec membranes and a steel tank and available in various litres/day per day output.
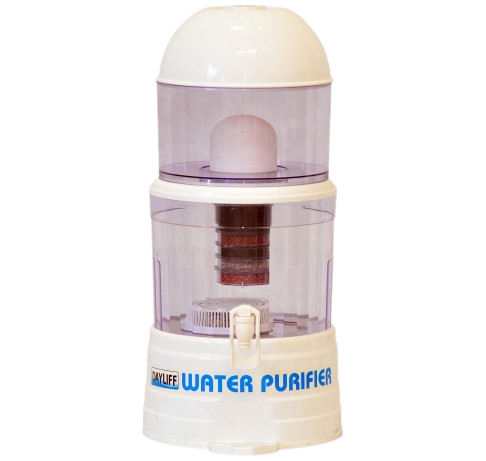


Mineral Water Pot Water Purifier
A mineral water pot is a gravity feed 8 stage purifier to provide quality drinking water from municipal sources-simply pour water in at the top and enjoy pure healthy water at the outlet. Flow is approximately 30L/day and total capacity is 14L with 9L of treated water storage.
The treatment process includes:-
- Fine ceramic filter for light silt and bacteria removal.
- 5 level multi media cartridge for taste and odour conditioning.
- Zeolite based water softening.
- Mineral module to add essential minerals to the water making it healthy and giving it a fresh taste.
- Magnetic Water tap to enhance the absorption to nutrients and supplements in the body cells.

